Injectable manufacturing is a high-precision process where patient safety and product efficacy are non-negotiable. Contamination, sealing failures, or formulation instability can jeopardize compliance and market success.
This article explores the most pressing challenges in injectable production and provides actionable, expert-backed solutions to ensure quality and reliability.
Why Injectable Manufacturing is High-Stakes
The production of pharmaceutical injectables demands stringent standards due to their direct administration into the body. Even minor errors can lead to severe consequences, including regulatory penalties, product recalls, or patient harm.
By addressing key hurdles proactively, manufacturers can achieve compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and build market trust.
Key Challenges and Proven Solutions
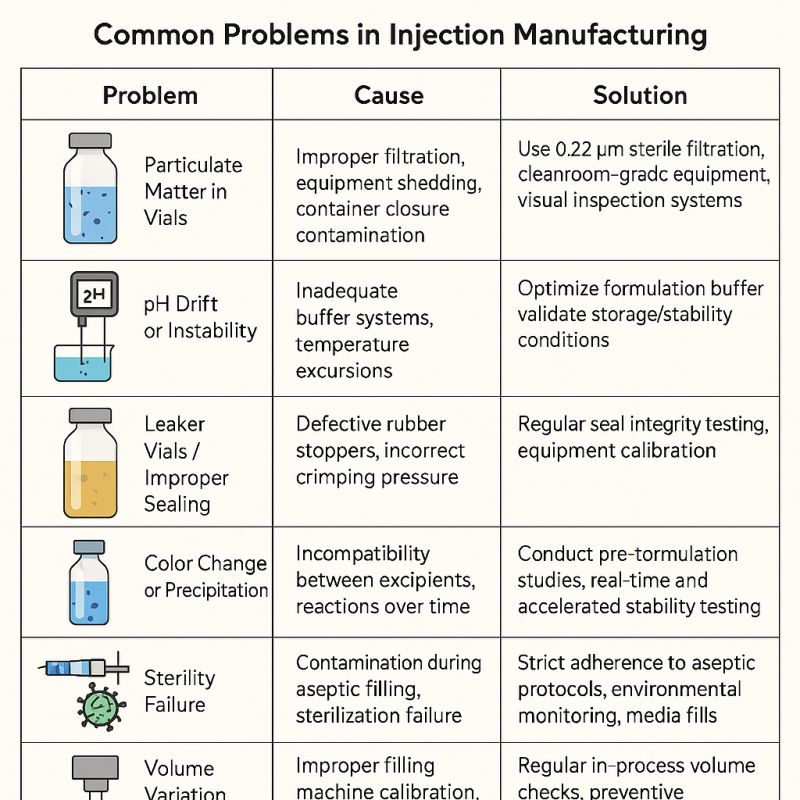
The following table outlines the top challenges in injectable manufacturing, their root causes, and effective strategies to overcome them:
| Challenge | Root Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Matter in Vials | Inadequate filtration, equipment debris | Implement 0.22 μm sterile filtration, use cleanroom-grade equipment |
| pH Drift or Instability | Weak buffer systems, temperature fluctuations | Optimize buffer formulations, validate storage conditions |
| Leaker Vials/Sealing Issues | Defective stoppers, improper crimping | Perform routine seal integrity testing, validate stopper-crimping processes |
| Color Change/Precipitation | Excipient incompatibilities, time-dependent reactions | Conduct pre-formulation and accelerated stability studies |
| Sterility Failure | Contamination during aseptic filling | Enforce rigorous aseptic protocols, monitor cleanroom environments |
| Volume Variation | Miscalibrated filling equipment | Calibrate machines regularly, implement preventive maintenance schedules |
Strategies to Streamline Injectable Production
To tackle these challenges effectively, manufacturers can adopt the following proven strategies:
1. Implement a Robust Quality Management System (QMS)
- Align operations with GMP guidelines to ensure consistent product quality.
- Use real-time monitoring to detect deviations early and maintain compliance.
2. Utilize Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Identify underlying issues behind recurring problems, such as contamination or equipment failures, using RCA techniques.
- Apply corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) to eliminate risks systematically.
3. Invest in Workforce Training
- Train staff on advanced aseptic techniques to minimize human error in cleanrooms.
- Conduct regular skill assessments to maintain high operational standards.
4. Ensure Equipment Validation
- Complete Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ) for all critical equipment.
- Schedule preventive maintenance to avoid unexpected downtime or calibration issues.
Expert Tips for Long-Term Excellence
To stay ahead in injectable manufacturing, consider these proactive measures:
- Conduct Regular Audits: Perform internal and third-party audits to identify compliance gaps and process inefficiencies.
- Integrate Advanced Technologies: Adopt automated filling systems and real-time environmental monitoring to enhance precision and reduce risks.
- Prioritize Stability Studies: Test formulations under varied conditions to predict and prevent issues like precipitation or pH drift.
- Foster a Culture of Quality: Encourage continuous improvement through employee feedback and cross-departmental collaboration.
Conclusion: Building a Future-Ready Manufacturing Process
By addressing these critical challenges with targeted solutions, manufacturers can ensure their injectable products meet global regulatory standards and deliver safe, effective outcomes for patients. Implementing robust systems, leveraging cutting-edge technologies, and fostering a quality-driven culture will not only secure compliance but also strengthen market credibility.
Take action today to transform your injectable manufacturing process and lead the industry in quality and innovation.


